Axillary Breast Tissue
What is Axillary Breast Tissue
What is Axillary Breast Tissue
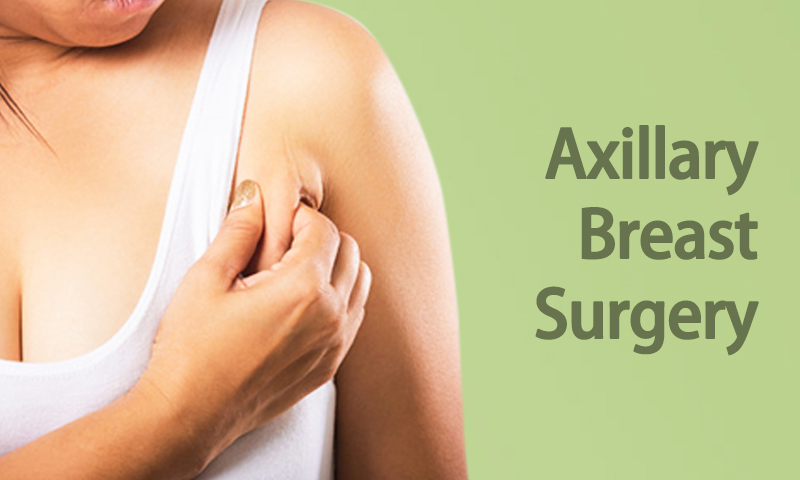
Axillary breast tissue refers to the area on either side of the breastbone, composed mainly of lymph nodes, serous (watery) glands, and fat. Axillary breast tissue can contain cancer cells that have spread from a primary tumor elsewhere in the body, as well as benign conditions such as cysts or benign lumps called fibroadenomas.
Axillary breast tissue is any excess or abnormal growth of breast tissue in the area under the arm, known as the axillary region.
Axillary breast tissue is composed of the armpit and underarm fat that you may here call “bat wings”. It’s generally easier to safely lose weight in your arms and your chest than it is in other areas of your body because of this axillary breast tissue, especially if you’re between two sizes.
The best way to lose weight in your arms is by doing exercises that work the muscle. These include pushups, triceps dips, and other arm exercises you can do with just your body weight.
In addition, try to incorporate some cardiovascular activity such as running or walking into your fitness routine a few times per week. When you’re trying to lose weight in your chest area, it’s important to remember that it isn’t just about losing fat. You also want to make sure that you’re building muscle mass so that you don’t look too skinny once the fat disappears from around your breasts.
What causes axillary breast tissue?
Axillary breast tissue is caused by an excess of fat deposits in the chest area. It’s common in women who are overweight or obese, and it can also occur when you have too much body fat for your height. In most cases, axillary breast tissue is only noticeable when a woman wears tight-fitting clothing that highlights her bust line.
Axillary breast tissue is a common cause of breast pain, tenderness, and swelling in women. Axillary breast tissue gets its name from the axilla, which is the space below the upper part of your arm. In most women, it does not produce milk but can be felt under the skin during a physical exam.
Axillary breast tissue is the area of the mammary gland between the chest wall and the pectoralis muscle. It includes an axillary tail, terminal and lateral ductules, interlobular ducts, and the peripheral part of the lobule. Axillary breast tissue is important in the formation of milk. It is also targeted for lymph node dissection in breast cancer surgery.
Causes of Axillary Breast tissue
The most common cause of axillary breast tissue is a condition called pseudogynecomastia. This type of abnormality occurs when fat is deposited in the chest area, where it has no business being. It can also occur due to obesity or simply having too much body fat for your height (called “adipose hypertrophy”).
Lipoma: A lipoma is a benign tumor made up of fat cells. It usually forms in the subcutaneous tissue, but can also occur in other areas of your body. A lipoma can be as small as a pea or as large as an orange. Lipomas are painless unless they press on nerves or blood vessels. They are most often found on the back of the arms, shoulders, and neck; less commonly, they’re found on the trunk (chest) and abdomen.
Abnormal growth due to genetics: Some people are born with a genetic disorder that causes abnormal growth. These conditions include neurofibromatosis, McCune-Albright syndrome, and certain types of bone diseases. Abnormal growth due to genetics can also lead to Langerhans cell histiocytosis, which is characterized by a proliferation of immature white blood cells called Langerhans cells.
A tumor or cyst: Some growths are benign, but others can be cancerous. If you notice a lump that doesn’t go away, see your doctor so he can diagnose it and determine the best treatment plan for you.
Hidradenitis suppurativa: This is a skin condition that causes painful abscesses, boils, and cysts to form on the apocrine sweat glands in your armpits, groin area, or buttocks. It’s caused by inflammation of these glands, which can occur when they become clogged with dead skin cells.
Vascular malformation: A vascular malformation is a cluster of abnormal blood vessels that can cause pain, a mass, or bleeding. It’s most often found in the soft tissues of your body, but it can also occur in internal organs like the liver, lungs, and brain.
Is axillary breast tissue dangerous?
Yes, axillary breast tissue is dangerous. Axillary breast tissue can cause serious problems if it’s not diagnosed and treated early on. This type of breast cancer can spread to lymph nodes in your armpit areas and other parts of your body that contain lymph nodes, such as the lungs, liver, and brain.
If you have a lump or swelling in your armpit, it’s important to see a doctor right away. Many cancers start in the lymph nodes and spread to other parts of the body through lymphatic fluid.
If you have axillary breast tissue and it’s not diagnosed and treated early on, your chances of survival are lower than they would be if the tissue was treated right away.
Axillary breast tissue symptoms
It includes a lump or swelling in your armpit. You may also notice that the area around the lump becomes tender, red, and warm to the touch. You may feel pain in your armpit when you move or touch it. Other signs of axillary breast tissue include:
- A lump or swelling in your armpit area.
- Pain, tenderness, or unusual firmness in one of your breasts.
- Nipple discharge that is bloody, green, or black.
- Skin changes on your breast, such as dimpling or puckering.
- A rash or darkening of the skin around your nipple.
- A breast lump that grows rapidly or is painful.
- Breast pain is severe and lasts for more than a few hours.
- A breast lump that moves when you press on it.
- A new breast lump or mass that does not go away after several months.
- Pain in your armpit area or upper chest that doesn’t go away when you move or touch it.
Best Surgeon

Dr M. Shridharan
(MBBS, MS, MCh – Plastic Surgery with 22 Years Experience)
How to Reduce Axillary Breast Tissue Naturally
Axillary breast tissue removal without surgery
Axillary breast tissue is a possible treatment option for breast cancer that has spread to the axillary lymph nodes. This procedure is called sentinel lymph node biopsy. It’s done by injecting dye into your arm and then taking pictures of your lymph nodes under a microscope. If there are cancer cells in the nodes, they will show up on the images.
Axillary breast tissue removal without surgery is a treatment option for some women who have dense breast tissue or other conditions that make mammograms difficult. It allows radiologists to see areas of the breast that are otherwise hidden by dense tissue. Axillary breast tissue can be diagnosed with dye markers, which highlight blood vessels in the area.
If you have axillary breast tissue and want to find out more about your options, please contact us today to schedule an appointment with one of our board-certified plastic surgeons in Chicago who specialize in all aspects of breast health.
Radiologists can use various methods to detect axillary breast tissue, including:
-A biopsy of the fatty area around the nipple and areola.
-Dye markers that highlight blood vessels in the area.
-Ultrasound, which uses sound waves to create an image of the breast.
-MRI scans and CT scans, use magnetic fields to create images of the body’s structures.
Axillary breast tissue exercise
Axillary breast tissue exercise is generally safe and can be done as often or as little as you like. However, it’s important to note that your doctor may recommend limiting certain types of exercise if they pose a risk for injury or pain in this area.
For example, swimming is typically considered safe because it doesn’t put pressure on the breasts, but contact sports like football could be problematic because they can cause bruising or other injuries to axillary tissue.
Axillary breast tissue exercise is an easy and effective method to strengthen your arm muscles. This exercise is useful for strengthening the pectoralis minor muscle, which supports the position of the breast tissue and prevents sagging breasts.
By strengthening this muscle, you can effectively combat the effects of aging and gravity on your breasts. You should perform axillary breast tissue exercises for about 5 to 10 minutes each day or as recommended by your doctor.
In addition to the pectoralis minor muscle, two other important muscles support breast tissue: the serratus anterior and the rhomboid major. These muscles work together to keep your breasts from sagging and provide them with a youthful shape. These muscles need to be strong for your chest to look toned and firm.
What is Axillary Breast Tissue
Axillary Breast Tissue in Armpits Treatment
Axillary breast tissue treatment is for patients who want to remove one or two lymph nodes in the armpits. This treatment can be done under local anesthesia and does not require a hospital stay. Lymph nodes help fight infection and may contain cancer cells.
Axillary breast tissue treatment is the most common treatment for sagging breasts. It works by tightening the skin and underlying ligaments of your chest, which helps prevent breast tissue from sagging. During a procedure, a surgeon uses an instrument to insert a small amount of fluid into each breast. The fluid stimulates collagen production in the area and increases firmness over time.
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, although some patients may require general anesthesia. It takes about an hour and a half to complete. When you meet with your plastic surgeon before your surgery, they will discuss the benefits and risks associated with axillary breast tissue treatment as well as any other options available for treating saggy breasts.
The procedure is a very safe, non-invasive treatment that can be used to improve the appearance of sagging breast tissue. It is typically performed in combination with other cosmetic surgery procedures such as breast augmentation or reduction.
Axillary breast tissue removal cost in Hyderabad
Axillary breast tissue removal surgery is an important procedure to restore your body shape and size. After the removal of the axillary breast tissue, there will be a visible change in breast appearance; your skin and nipple look normal, but they are smaller due to tissue reduction. You can wear a bra or swimsuit of your choice after this procedure that gives you a shape similar to that of a small chest.
The cost of axillary breast tissue removal in Hyderabad can vary depending on your surgeon’s experience, the type of procedure you are undergoing, and whether there are any complications. The average price is around Rs.60,000-70,000 for this procedure.
Conclusion
At Medini Cosmetic Surgery we believe that women should be able to make their own decisions about their bodies. We are committed to providing our patients with the best possible care, so they feel confident about themselves and their bodies.
We work with a team of highly experienced surgeons and other medical professionals who provide the best possible care and treatment for all patients. If you are looking for axillary breast tissue removal in Hyderabad, visit us today or contact us for an appointment. We are happy to help you
